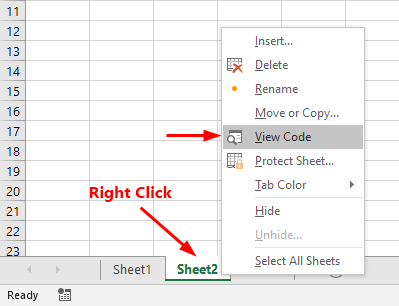
The worksheet event-handler procedures must be in the code module for that worksheet. Put them somewhere else, and they won’t work. You can quickly access that code window by right-clicking the worksheet’s tab and selecting the View Code:
Worksheet_Change event procedure
The Change event triggers whenever any cell in the worksheet is changed. Excel uses the Worksheet_Change event-handler procedure to trap the Change event. The Worksheet_Change procedure accepts Target (the Range object) as the parameter which represents the cell that was changed. The following example displays a message box that shows the address of the Target range:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range) MsgBox Target.Address End Sub
Try making some changing in cells, every time you make changes, a message box displays the address of the cell that changed.
Monitor changes made to specific cell or range
The Worksheet_Chnage procedure receives the Target as Range object which represents the changed cell(s). In this example, we compare the Target with the given cell range A1:A10 using Intersect method:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim MyRange As Range
Set MyRange = Range("A1:A10")
If Not Intersect(Target, MyRange) Is Nothing Then
MsgBox ("You've changed the " & Target.Address)
End If
End Sub
A popup message box appears when a change made in the given cell range:
Worksheet_Change Vs. Worksheet_Calculate
The Worksheet_Change event procedure is not executed by a calculation change, for example, when a formula returning a different value. You must use the Worksheet_Calculate event procedure to capture the changes to values in cells that contain formulas.
Worksheet_SelectionChange event procedure
The Worksheet_SelectionChange event procedure executes when a cell is selected. The following code highlights the active cell with a red color every time a different cell is selected:
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range) Cells.Interior.ColorIndex = 0 Target.Interior.ColorIndex = 3 End Sub
The first statement removes the background color for all cells in the worksheet. Next, the the active cell is shaded with red color.
Take some action when specific cells or ranges selected
In many cases, you need to execute a piece of code when certain cells or ranges selected. To accomplish this, we use the Intersect method on the Target (selected cell or range) and the range containing the specific cell to verify the Target is one of the specific cells or ranges. If the Target is in the range containing the specific cells, you can execute the code.
The following code highlights the active cell with a red color every time a different cell is selected:
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
Cells.Interior.ColorIndex = 0
Dim MyRange As Range
Set MyRange = Range("A1:A10")
If Not Intersect(Target, MyRange) Is Nothing Then
Target.Interior.ColorIndex = 3
End If
End Sub